Key Takeaways
- Rotary gear pumps provide consistent and precise flow rates, which are essential for processes requiring exact dosing.
- They efficiently handle high-viscosity fluids, reducing the risk of blockages and ensuring smooth operations.
- Their compact design and durability lead to lower maintenance costs and extended service life.
Efficient fluid transfer is a necessity across numerous industrial sectors, and rotary gear pumps have emerged as a vital asset in achieving this goal. These pumps are noted not only for their robust power but for the high degree of precision they bring to fluid movement. Renowned for their consistency and reliability, rotary gear pumps are widely deployed wherever controlled, uninterrupted flow is crucial, such as in manufacturing, chemical production, and other process industries that cannot afford unexpected downtime or variation in dosing. For example, rotary gear pumps are a key product offered by CandB Equipment, a leader in providing robust pumping solutions for demanding environments. Their expertise with rotary gear pumps allows industries to optimize processes and enhance performance, especially in difficult or hazardous working conditions.
The design and operational benefits of rotary gear pumps make them well-suited for industries requiring consistent output, minimal maintenance, and the flexibility to manage a broad range of fluid types. Their versatility is especially advantageous for companies working with both thin and highly viscous liquids, or those that frequently change production lines and need reliable, low-maintenance equipment. The presence of rotary gear pumps in sectors such as chemical processing, oil and gas, printing, and food production is a testament to their adaptability, reliability, and overall efficiency. Whether transferring aggressive chemicals, edible oils, or even ink, these pumps stand out as a preferred choice for fluid transfer across a spectrum of demanding applications.
Understanding Rotary Gear Pumps
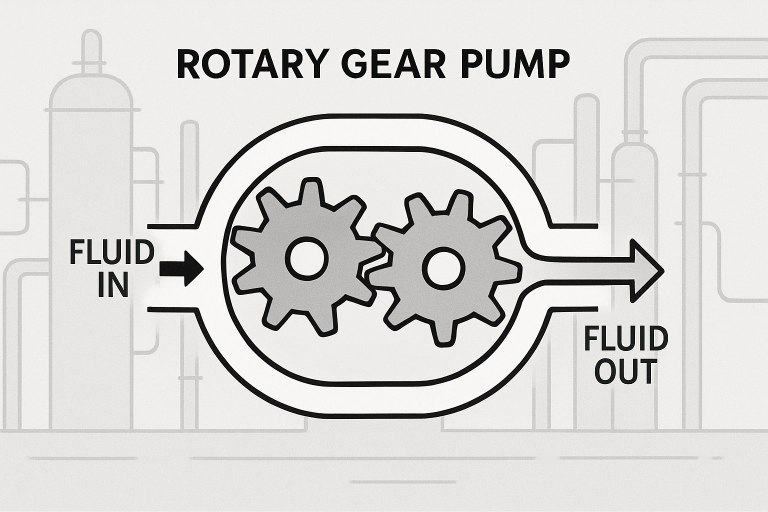
Rotary gear pumps operate on a simple yet effective principle involving two intermeshing gears housed within a tight casing. As these two gears—typically called the driving and driven gear—rotate in opposite directions, they create a partial vacuum at the pump inlet, drawing fluid into the voids between the gear teeth and the casing. This fluid is then smoothly transported around the casing toward the discharge port, where it is expelled in a steady stream as the gears mesh again. This positive displacement mechanism ensures a highly controlled and pulsation-free flow, which is especially valuable in scenarios demanding careful dosing, blending, or metering. The lack of pulsation also protects sensitive downstream equipment and helps maintain stable pressure throughout the process system.
The construction of rotary gear pumps, with their few moving parts and tight internal tolerances, leads to high volumetric efficiency and consistency over time. Their ability to maintain performance even with wear or changes in operating conditions sets them apart from many other pump types. Furthermore, variations such as internal and external gear pumps cater to a range of pressures, flow rates, and fluid properties, enhancing their utility across industries. The gear pump’s inherent simplicity also means fewer potential points of failure, supporting high reliability in continuous duty cycles or automated process lines.
Advantages in Industrial Applications
Accuracy in fluid delivery is a cornerstone of many industrial processes, from blending chemicals to filling bottles. Rotary gear pumps excel in delivering a consistent and precise flow, regardless of variations in back pressure or fluid viscosity. This makes them a trusted choice in chemical manufacturing, where combining and metering different chemicals in exact proportions ensures safety and product quality. In the food and beverage industry, the ability to dispense syrups or sauces in controlled quantities is vital not only for taste and texture but for regulatory compliance in nutritional labeling. Unlike centrifugal pumps, which can fluctuate with changes in pressure, gear pumps maintain an almost linear output relative to their speed, making them ideal for dosing and batch processes where every drop counts.
Precision in fluid delivery also contributes to reducing waste, a critical concern in costly or hazardous materials. By minimizing variation and overuse, companies can achieve better cost control, consistent product output, and increased overall efficiency.
Fluids like oils, molasses, adhesives, and resins can be challenging for standard pumps due to their viscosity, which implies resistance to flow and a tendency to clog or cause cavitation in less robust pump types. Rotary gear pumps are specifically engineered to tackle these challenges—moving thick, heavy, or sticky substances with relative ease while maintaining steady output. The tight clearances and strong suction created by intermeshing gears enable gear pumps to transfer viscous or heavily laden fluids without significant drops in efficiency.
This capability greatly enhances process efficiency, particularly in sectors like adhesives (where air bubbles must be avoided), petrochemicals (where crude oil must flow reliably under varying temperatures), and specialty foods (such as honey or syrup transferring). Gear pumps’ ability to handle suspended solids and high viscosity also reduces the risk of blockages, equipment wear, and downtime—problems that can lead to expensive repairs, product loss, or line shutdowns.
Compact Design and Durability
Rotary gear pumps ‘ compact footprint proves invaluable when facility space is at a premium or installation flexibility is required. Their robust construction materials—ranging from stainless steel to specialized alloys and engineered polymers—are designed to withstand the corrosive effects and abrasive nature of many industrial fluids. Whether processing acidic chemicals, fuels, or abrasive slurries, rotary gear pumps offer impressive longevity and reliability.
This durability translates directly to lower total cost of ownership. Fewer breakdowns, less frequent servicing, and proven long-term reliability mean less downtime and smaller maintenance teams. This is a key advantage for plants operating in remote or hazardous locations, where quick repairs may not be feasible, and for organizations seeking to maximize return on investment by minimizing lifecycle costs.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Operating efficiency is critical to controlling manufacturing costs, especially in energy-intensive industries. Rotary gear pumps are engineered to minimize power consumption by optimizing internal geometry for maximum flow with minimal internal leakage or hydraulic loss. Their simple mechanical motion and positive displacement design translate into higher energy efficiency compared to many centrifugal or reciprocating pumps, particularly when working with higher viscosities or moderate flow rates.
The ability to handle a diversity of fluids with consistent efficiency means plants can standardize on fewer pump models, streamlining both inventory and maintenance requirements. Furthermore, lower energy consumption directly reduces operational expenses and greenhouse gas emissions. For companies aiming to achieve sustainability targets or comply with increasingly strict energy regulations, the use of energy-efficient rotary gear pumps can have a significant and measurable impact. Their renowned reliability and efficiency also limit the frequency of costly breakdowns and emergency repairs, allowing maintenance teams to focus on predictive and preventative strategies that add value to the business.
Real-World Applications
In the oil and gas sector, rotary gear pumps are entrusted with a variety of vital tasks—fuel transfer, lubricating machinery, and handling both crude and refined products. Their capacity to maintain accurate, field-proven flow under wide-ranging pressure and viscosity conditions ensures steady, predictable operations, which is crucial for maximizing productivity and minimizing risk. In the food and beverage world, rotary gear pumps are indispensable for moving thick substances like syrups, chocolate, and concentrated mixtures. These pumps prevent the introduction of air or contaminants and help ensure consistently high product quality. Their sanitary versions are built with smooth, easy-to-clean surfaces to meet rigorous safety standards required in sensitive production areas.
Beyond these well-known uses, rotary gear pumps are found in ink circulation for printing presses (where viscosity and flow stability affect print quality), in paint and coatings manufacturing (where clog-free, even transfer is critical), and even in pharmaceutical production (where sterility and precision are paramount). The gear pump’s adaptability to specialized applications demonstrates its advantages wherever fluid transfer demands are challenging or unusual. Their reliability and performance enable diverse industries to maintain productivity and meet ever-tightening standards for product quality and safety.
Conclusion
The role of rotary gear pumps in driving efficiency and productivity in industrial settings cannot be overstated. Their ability to deliver consistent flow, handle high-viscosity materials, and minimize both energy and maintenance costs makes them an essential asset in modern production processes. Businesses looking to enhance process reliability and efficiency can confidently rely on rotary gear pumps as a core component of their fluid transfer systems. As industrial operations continue to evolve and demand higher performance, the enduring utility of rotary gear pumps positions them at the forefront of efficient, reliable, and economical fluid transfer solutions.



